Demystifying SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and Platforms: Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model
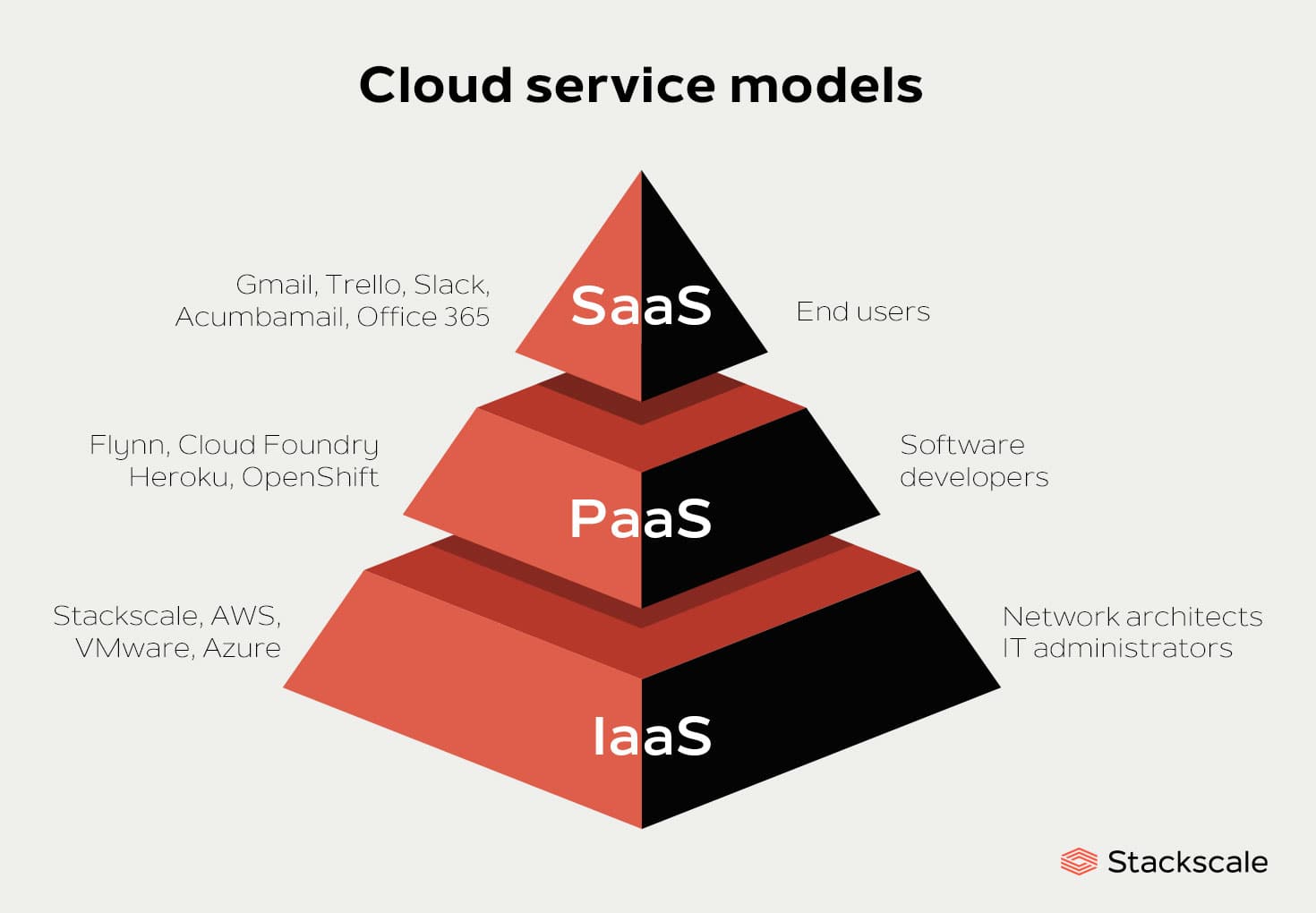
The advent of cloud computing has dramatically transformed the operational dynamics of businesses worldwide. Providing a spectrum of versatile service models, cloud computing allows businesses to select offerings tailored to their specific needs. Key cloud service models include Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), and a myriad of specialized platforms. This blog post delves into the distinctive characteristics, inherent benefits, and ideal use cases of each cloud service model to facilitate informed decision-making when adopting cloud services for your business.
We'll now delve deeper into each cloud service model, exploring their nuances and value propositions:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS):
SaaS is an epitome of the "plug-and-play" ideology in the cloud service realm. Offering ready-to-use software applications via the internet, SaaS offloads the tasks of software installation, maintenance, and infrastructure management to the service provider. Key advantages of SaaS include rapid deployment, significantly reduced upfront costs, and automated software updates. It offers businesses the freedom to focus their resources on leveraging the software to achieve their operational objectives without the distractions of infrastructure management. SaaS is especially advantageous for small to medium-sized businesses and those striving for hassle-free software management.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS):
PaaS stands as a comprehensive ecosystem for application development, testing, and deployment. It delivers a cohesive environment inclusive of infrastructure, an operating system, a runtime environment, and essential development tools. PaaS effectively abstracts the intricacies of infrastructure management, enabling developers to focus solely on crafting efficient applications. Key features such as scalability, collaborative capabilities, and automated deployment streamline the application development process. PaaS is an ideal solution for businesses aiming to expedite application development, improve teamwork efficiency, and minimize infrastructure management overheads.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS):
IaaS embodies the provision of virtualized computing resources over the internet. This includes virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities. IaaS endows businesses with the flexibility to scale infrastructure resources based on evolving needs, ensuring cost-effectiveness by charging only for the consumed resources. With IaaS, businesses gain extensive control over their infrastructure, allowing them to customize configurations and manage their applications and operating systems. It's well-suited for businesses demanding high levels of control, fluctuating infrastructure requirements, or those aiming to transition existing applications to the cloud.
Specialized Platforms:
Going beyond the standard cloud service models are specialized platforms, often referred to as "as-a-Service" (PaaS+) models. These platforms augment the core cloud infrastructure with additional services and capabilities, tailored to address unique business requirements. These may encompass specialized tools, frameworks, or APIs that facilitate efficient application development, deployment, and management. For instance, Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) platforms offer access to curated datasets and sophisticated data analytics tools. Integration-as-a-Service (IaaS) platforms ensure seamless integration with other systems and services. Communication-as-a-Service (CaaS) platforms provide robust communication and collaboration tools. Specialized platforms enhance the utility of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS models and cater to specific industry verticals or application domains.
Conclusion:
Grasping the distinct features and benefits of SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and specialized platforms is integral to making informed decisions when adopting cloud services. Each model carries unique advantages and is designed to cater to different business needs. Weighing factors such as scalability requirements, available development resources, desired control levels, and specific functionalities will guide businesses towards the most suitable cloud service model or platform.
The adoption of cloud services endows businesses with enhanced flexibility, scalability, reduced infrastructure costs, and the freedom to concentrate on their core competencies. By making the right choice of cloud service model, organizations can spur innovation, maintain agility, and foster growth in today's fast-paced digital era.
Comments
Post a Comment